For New York patients needing a tooth extraction, immediate implants are a predictable means of tooth replacement. Immediate implants result in similar tooth survival rates compared to delayed implants and excels at preserving tissue and produces functional and aesthetically pleasing outcomes much faster.
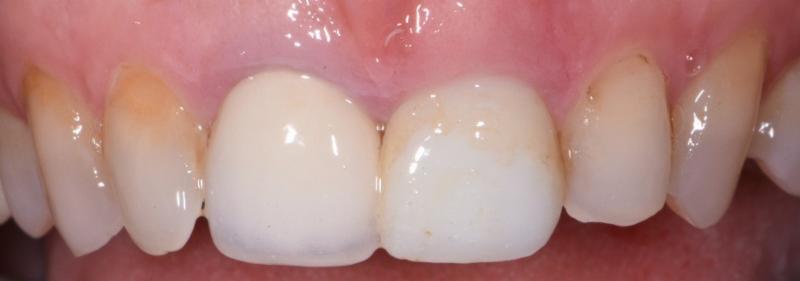
This patient was referred to the New York City office to remove tooth #9, it was carious and had a hopeless prognosis. This tooth also displayed a short clinical crown. This etiology of short clinical crown can be from a pathognomonic short anatomic crown, attrition, or altered passive eruption. In this case, the diagnosis was altered passive eruption (APE), the free gingival margin failed to recede during normal tooth eruption. This occurs in about 12% of patients.
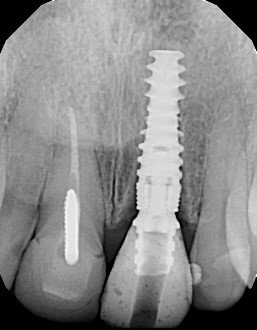
There are different classifications of APE, and this patient has a Coslet Type 1B. This is when the alveolar crest is at the cementoenamel junction (CEJ), and there is a taller height of gingival tissue above the bone. Facial sulcus depth is 3mm, but the distance to the bone is about 4- 5mm. When evaluating a short clinical crown many diagnostic steps are necessary before prosthetic tooth borne or implant planning. One must consider the tooth form and position, bone relationship to CEJ, distance from bone to free gingival margin, sulcus depth, and thickness of soft tissues. This case is demanding because the gingival height of the central incisors is incisal to that of the laterals. A discussion needed to occur with this patient to determine if she was satisfied with the current esthetic appearance of her teeth or if she wanted the full anatomic crown of #8 exposed. This particular patient was happy with her current aesthetics and wanted the implant restoration to match tooth #8. If she had wanted #8 exposed, then bone reshaping would have been necessary at both #8, 9 sites to move the biologic width to a more apical region. If, after tooth removal, we need to keep the tissues in their current position, a tall band of tissue will need to be maintained above the bone. This will significantly increase the risk of future gingival recession. To further complicate the case, the cone beam shows her tooth position hugging a thin buccal plate of bone, and it was determined that the overlying gingiva was thin as well.
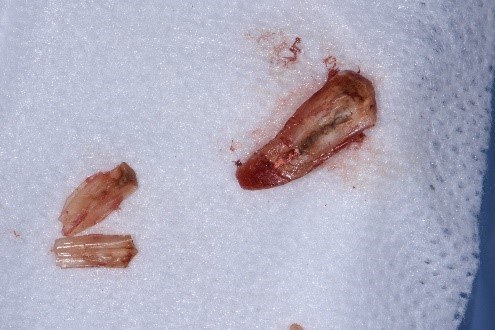
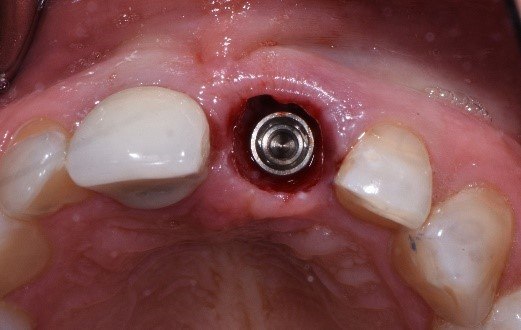
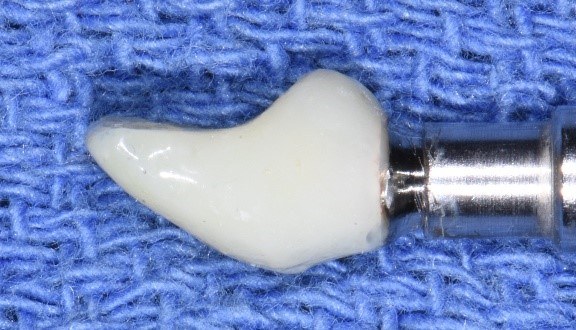
Our final treatment plan was to use microsurgery for all phases of treatment and an immediate implant. The tooth was carefully removed in sections. The immediate implant was positioned to allow for as much buccal bone graft as possible while at the same time recognizing her deep bite. Subsequently, a screw-retained composite provisional was fabricated which finally was followed by a connective tissue graft. The patient was advised that future recession is a risk. In this case, to minimize this risk, the buccal plate was preserved with atraumatic tooth removal. Bone and soft tissue grafts were placed, and a properly shaped provisional was created to support the soft tissue graft and provide proper emergence profile.
New York City patients regularly choose Dr. Kissel for tooth extraction and when they want a better smile. Immediate implants are a common technique to provide a better quality of care, and Dr. Kissel is an expert in the procedure.
Call (212) 702-9088 or stop in for a consultation and see what kind of care Dr. Kissel can provide for you.
Pre-Op Condition
Sectioned Root Micro-surgically
A traumatic tooth removal. Note: Tall tissue collar drooping into socket.
Flat buccal emergence to accommodate soft tissue graft and existing tissue thickness and position.
Screw retained composite provisional. Note: implant position relative to bone crest.
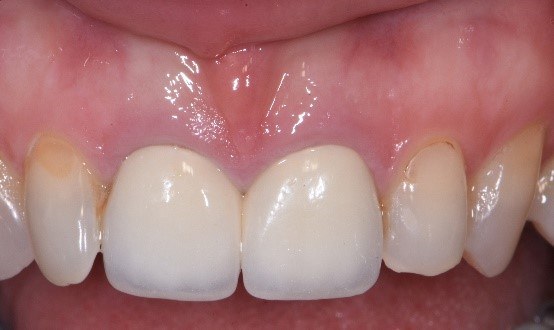
Two Month Post Op. A suture is visible helping to maintain tissue height on #9. Note: Some shrinkage is expected.